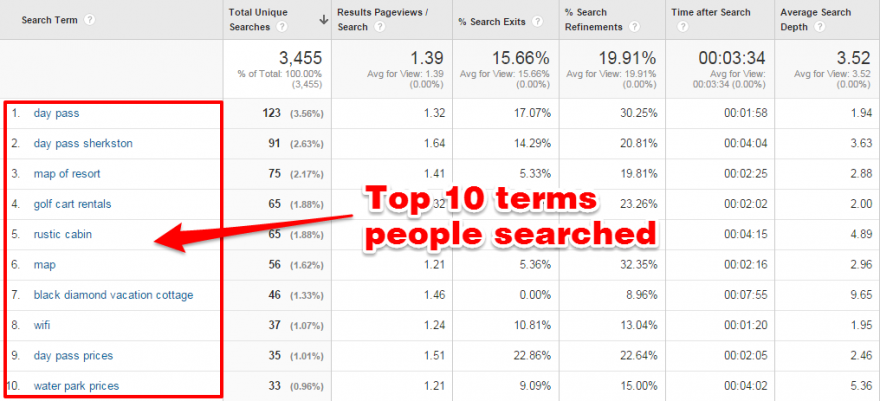
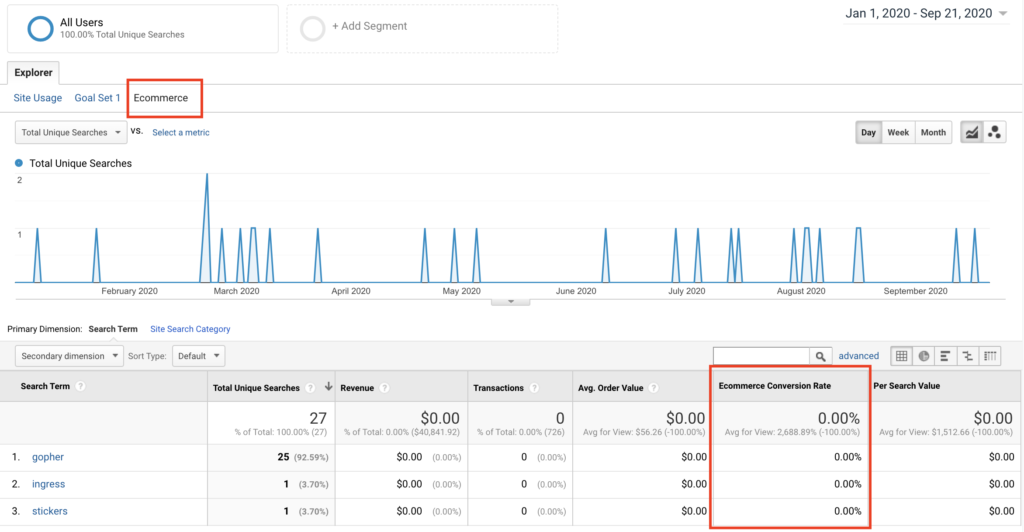
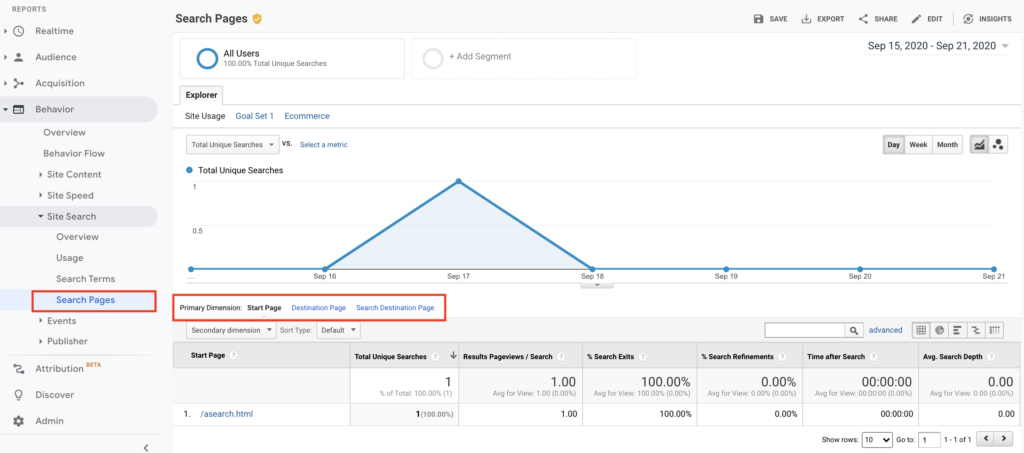
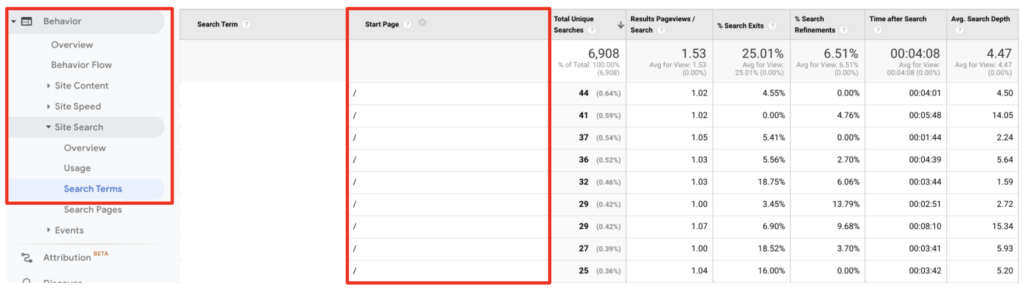
A user interview is a semi-structured interview method generally used in the exploration stage of a project. Understanding potential users, their daily lives, and most importantly the context of goals and motivations of potential users are essential discovery areas for the researcher.
What should I prepare for a user interview?
First, you can start by writing down what you’re trying to understand with the research, and the specific points you should understand deeply.
Let’s say you’re conducting research to enhance the user experience of a call center intranet, and you have to understand the main purpose of using the call center interfaces, but can’t directly ask the participant this question. Instead, you can prepare your questions by providing a context.
- “How do you start your conversation with the clients, and which screens are you using while you talk with them?”
- “Can you show me the process of mentioning critical parts and why they are so critical for you?”
- “Now conversely, please think of, and tell me about a particular time when you used the tool, and it made you ineffective in your work.”
- “Can you show me the process that made your call ineffective?”
These questions are more appropriate for user interviews because they provide a context and ask participants a process they regularly do and think about.
Review your prepared questions before the interview process. Make sure to conduct a pilot interview with one of your teammates and test the questions.
Why is a user interview important?
We need to understand our users, and the first thing to understand people is to empathize with them. Interviews provide a context to understand and evaluate the problems of the users. We can learn about the problems and challenges they’re facing directly from them. Therefore, we need to ask the right open-ended questions and listen to them.
Moreover, user interviews are a rich source of information to feed personas and further research that is going to be carried out after the discovery phase. For example, in usability testing, we ask follow-up questions to the user to understand the motivation behind their actions or to understand the dominant emotion in the experience. We select the participants from different personas for usability testing, and the user interviews that we conducted in the discovery phase become very beneficial at this point.
How long should qualitative interviews last?
A user interview generally takes 30 minutes to 1 hour. As we can understand from the name, we don’t have a strict time limit to finish the interview. As long as the interview is fruitful, the researcher can extend the time according to the daily schedule.
How many user interviews should you do?
What are you researching, and which context are you researching for? Some researches should have a wider sampling size due to having a larger number of user profiles. According to the NN group, you should make at least 5 user interviews. One of the leading resources the NN group states that after 5 interviews the findings start to repeat itself. So we can safely assume that if there is nothing “extraordinary”, 5 interviews are enough to analyze the patterns of the users’ behavior. As a researcher, if you can’t find any patterns that are repeating itself, maybe you can add new interviews to your schedule.
As much as you practice research your empathy skills and also interview skills will improve. User interviews are the fastest way to learn about users’ motivations and pain points. You can also learn about the potential users and the contexts they seek. It’s important to inform the participants about the research you do and prepare the right questions to provide accurate and reliable data.
As the VP of NN Group says;
UX without users isn’t UX.
Hoa Loranger